Good Scientific Practice¶
This chapter is based on the notes 2022-06-28_ConflictOfInterest_Plagiarism.pdf
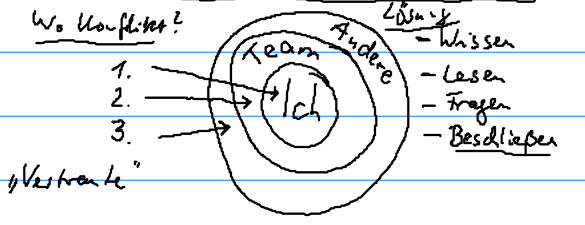
Conflict of Interest¶
Conflicts of interest through:
Friendship
Antagonism/hostile relationship
Dependence
Collaboration
Examples for conflicts of interest:
Reviewing:
Professional assessment
Helping a friend
Student representatives:
Representing the students’ interests
Own interests at University (grades, career, etc.)
Women’s representative
Lobbies
Politicians in board of directors:
Party
Company
Additional occupation or spare-time work:
First employer
Second employer/own company
Differentation in primary interests and secondary interests.
Example cases where conflicts of interest are important:
Research in company
BSc thesis in company
Peer-reviewing papers
Hiring decisions
Exam attestation
Solutions:
Form a committee, do not decide alone
Categorization of ‘conflict of interests’ by others, not yourself
Prevention of ill influence through anonymous reviews
Transparency (communicate potential conflicts)
Decisions should be correct, transparent and invulnerable.
Sources:
Example conflicts of interests strictly defined by DFG (German Scientific Organisation):
Spouse or close relative
Economic relationship
Scientific cooperation: Current or planned
Supervisor-supervisee relationship: Current or within the last six years
Work at relevant institution: Current or planned
Plagiarism¶
Definition: Theft of intellectual property.
Using others’ work
Completely or modified
Pretending to be the creator
Plagiarism in law:
Copyright
Compensation possible
Cease-and-desist letter
Sources must always be attributed, also for self-plagiarism!
Violation of good scientific practice
Plagiarism in Academia¶
Examples for plagiarism:
Tutor attests exam or thesis, recognizes plagiarism: Copy from webpage without citation (academic misconduct)
Text from book translated word-to-word
Examples for no plagiarism:
Group work
Characterization:
Basic principle: Independent work.
“Reuse without Reference”: Academic misconduct originates from the use of work that is not cited.
Plagarism vs. Self-Plagiarism
Rules and consequences must be defined and followed
IEEE rules (IEEE Ops manual, Section 8.2.4):
Level 1: Uncredited verbatim copy of more than 50% within single article
Notice of Violation published
Publication of work prohibited
Rejection of all of the authors’ articles currently under review (resubmission possible after plagiarism issue resolved)
Up to 5 years of prohibition of publication in all IEEE-copyrighted publications by the authors
Recommendation: Require Letter of Apology and publish it (if no letter written: 1-2 years additional prohibition of publication)
Level 2: 20%-50%
Same as above, but only …
Up to 3 years of prohibition of publication
Level 3: <= 20 %
Letter of Apology to plagiarized authors and publication editors (private)
Notice of Violation published
Possible action: Publication of Letter of Apology
Level 4: “Inappropriate paraphrasing” of significant portion
Same as above, but only …
Prohibition of publication in single venue if no Letter of Apology written.
Level 5: Verbatim copy without quotation mark
Correction required
Letter of Apology to plagiarized authors and publication editors (private)
Repeated violations: Up to a liftetime of prohibition of publication.
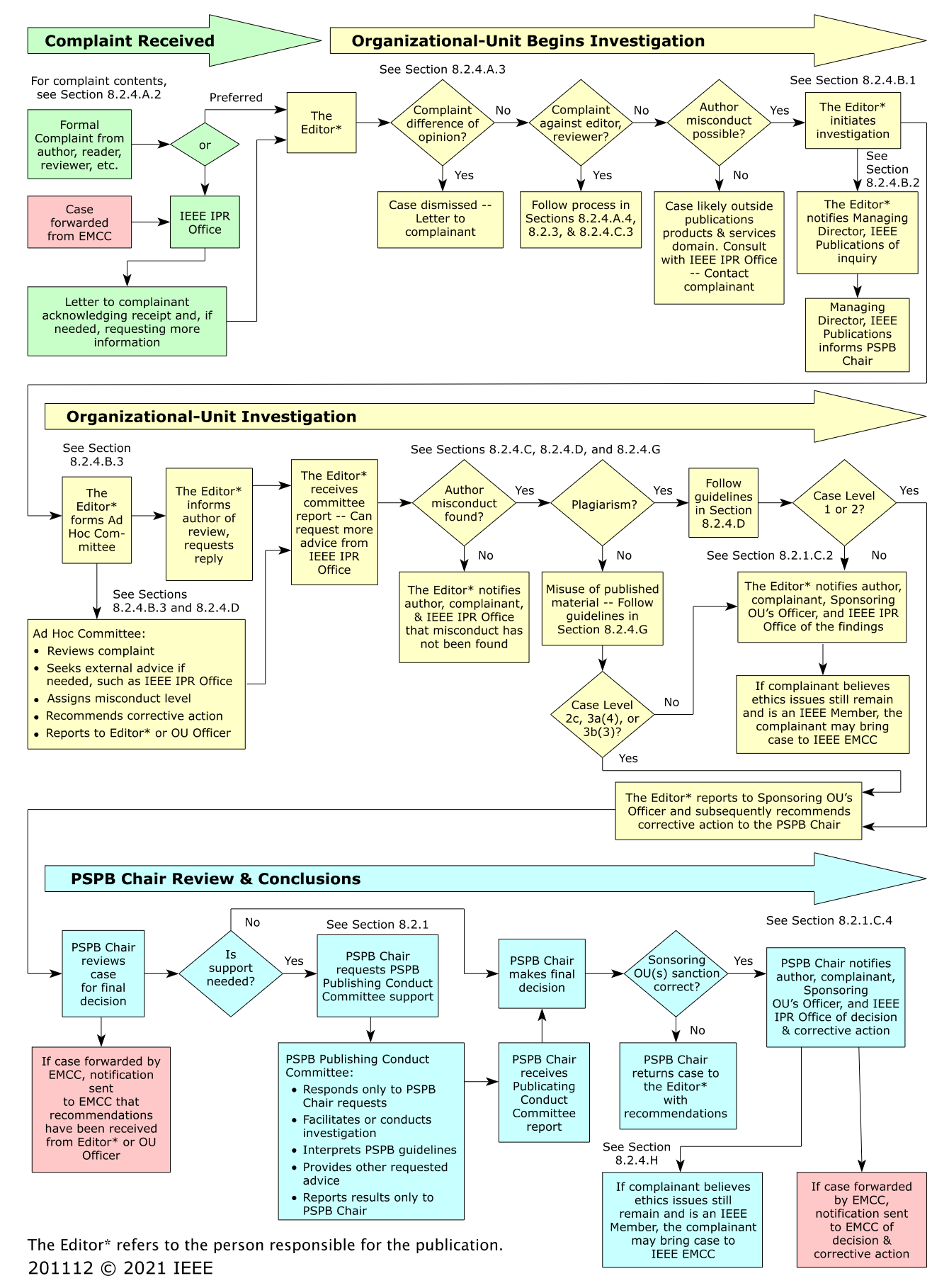
Process for misconduct handling by IEEE (Figure 8.2.4. in IEEE Ops manual):